Energy Talks by Sicame: Medium-voltage surge arresters – how to choose them and what you need to know about them?
Surge arresters are one of the key components of medium-voltage overhead power lines. Their role is simple: to protect the network against lightning-induced overvoltages (for example, from direct or indirect lightning strikes) and switching overvoltages that may occur during network operation.
Without a proper, effective arrester, the consequences can be serious, and damage may occur to:
- insulators,
- disconnectors,
- transformers,
- PAS cable insulation cover,
- as well as other important infrastructure elements.
For this reason, the use of surge arresters in medium-voltage networks is not an option, but a standard that is crucial for safety and continuity of power supply.
How to choose the right surge protector?
Many families of surge protectors from various manufacturers are available on the market, with numerous different designations.
You’re probably wondering now what the criteria are for selecting a surge protector and why it’s so important?
These are some of the most frequently asked questions we receive, so let us explain.
The first step is to verify the manufacturer’s markings. You can find this information on the nameplate (most often located on the bottom or top fitting).
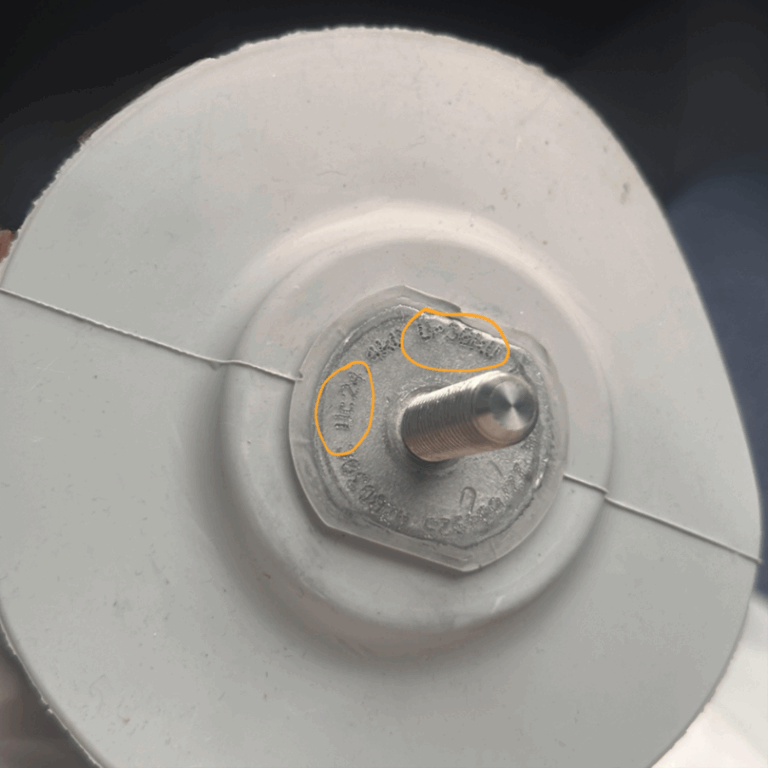
Szukaj dwóch kluczowych parametrów:
✅ Ur – rated voltage of the surge arrester
✅ Uc – continuous operating voltage
The parameter Uc defines the limit above which the surge arrester ceases to act as an insulator (at leakage currents in the milliampere range) and begins to conduct current.
Selecting the voltage Uc using the following example:
Example 1: ▶️ For a 15 kV line (nominal network voltage 17.5 kV) with an unknown short-circuit interruption time, Uc should be equal to or slightly higher than 17.5 kV.
Example 2: ▶️ For a 20 kV line (nominal network voltage 24 kV), Uc should be at least 24 kV.
This method allows you to safely select a surge protector even if you don’t have complete technical documentation for the network – for example, if you don’t know the disconnection time in case of a short circuit.
Remember – this is a simplification!
To fully verify the appropriate selection of the surge arrester, additional parameters should also be considered, such as:
- reduced voltage of the surge arrester (Ures),
- level of protection,
- short-circuit interruption time,
- environmental conditions,
- and other elements of network characteristics.
The method described above is a safe solution when information about the protected network’s parameters is unavailable. The more information you have about the line, the more precisely you can select the surge protector.
A proven solution: AZBD from Sicame Polska
For medium-voltage networks operating in demanding outdoor conditions, such as industrial areas or areas exposed to heavy pollution, the AZBD surge arrester from Sicame Polska is an excellent solution.
The AZBD surge arrester can be mounted horizontally, vertically, or on an insulating bracket, and in addition:
- It operates at surge voltages up to 100 kA (4/10 µs).
- It has high mechanical resistance (SSL: 250 Nm),
- It provides reliable performance across a wide temperature range: from –40°C to +60°C.
The external insulation made of HTV silicone and the compact design make it a solution that works perfectly in Polish climatic conditions – both in new and modernized energy infrastructure projects.
📘 You can find more information about AZBD in our SICAME Poland Product Catalog.
Want to learn more?
If you are unsure how to choose the right surge protector for your network, contact our team – we will help you select a product that will provide effective protection in all operating conditions.
📩 Contact us: sprzedaz@sicame.pl or biuro@sicame.pl
Follow our YouTube channel, where we share expert knowledge from the energy industry!









